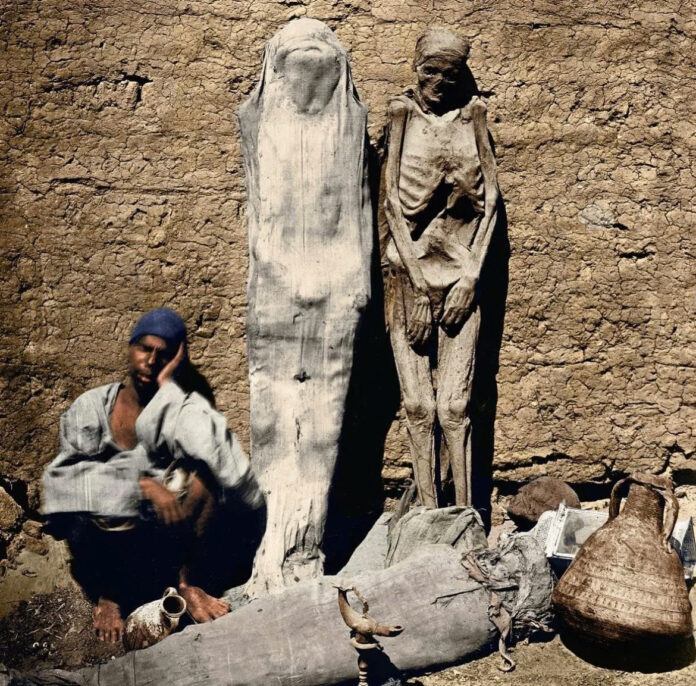
It was a scene that would seem unthinkable today: street vendors in 1865 Egypt openly selling mummies to European visitors. This unusual commerce marked a dark chapter in the treatment of ancient Egyptian artifacts, where sacred remains became commodities in a burgeoning and ethically questionable trade.
The Rise of Mummy Trading
Following Napoleon’s conquest of Egypt, European access to Egyptian antiquities expanded dramatically. However, this accessibility led to a disturbing trend where mummies, instead of being preserved and studied, became popular items for entertainment and various unusual applications.
Mummy Unwrapping Parties: A Victorian Entertainment
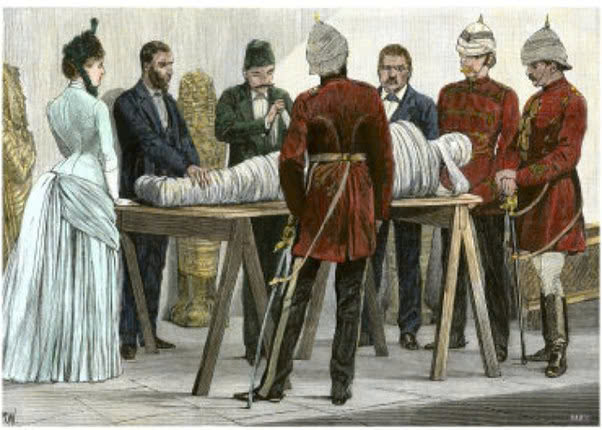

Among the elite social circles of Victorian Europe, “Mummy Unwrapping Parties” became a macabre form of entertainment. Wealthy hosts would invite guests to witness the unveiling of an Egyptian mummy, treating the desecration of ancient human remains as a spectacle. Attendees would watch with fascination as layers of ancient wrappings were peeled away, revealing the preserved remains beneath.
The Medicine Trade and Counterfeit Mummies
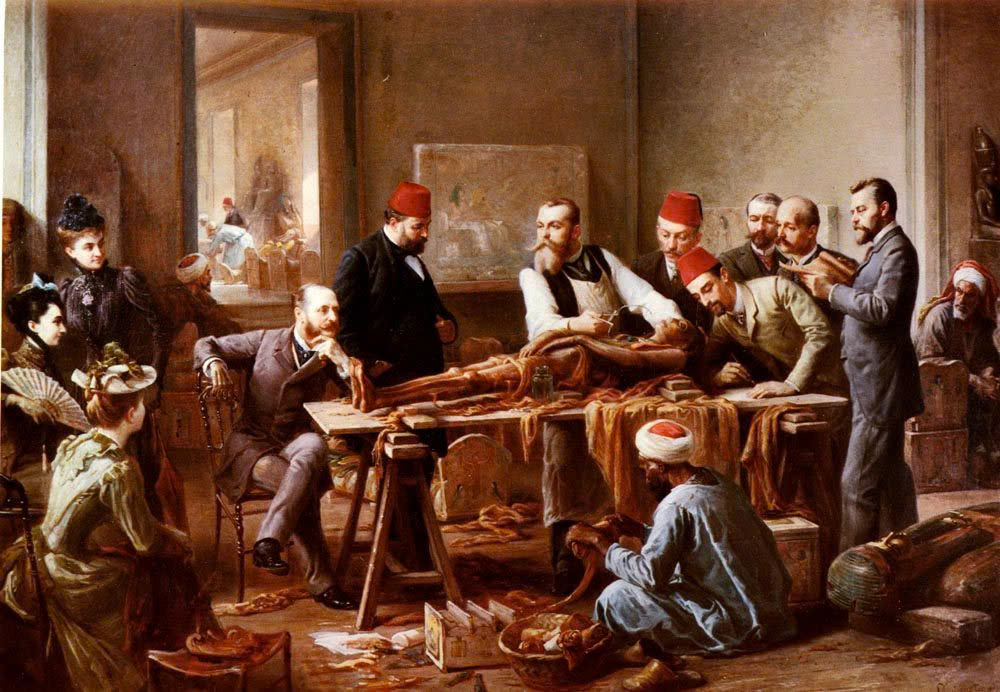

The demand for mummies extended beyond entertainment. A bizarre belief in their medicinal properties led to mummies being ground into powder for consumption. This demand sparked a shadowy trade in counterfeit mummies, where the bodies of recently deceased individuals, including executed criminals and disease victims, were processed to resemble ancient Egyptian remains.
Industrial Applications: From Sacred to Utilitarian
Fertilizer and Fuel
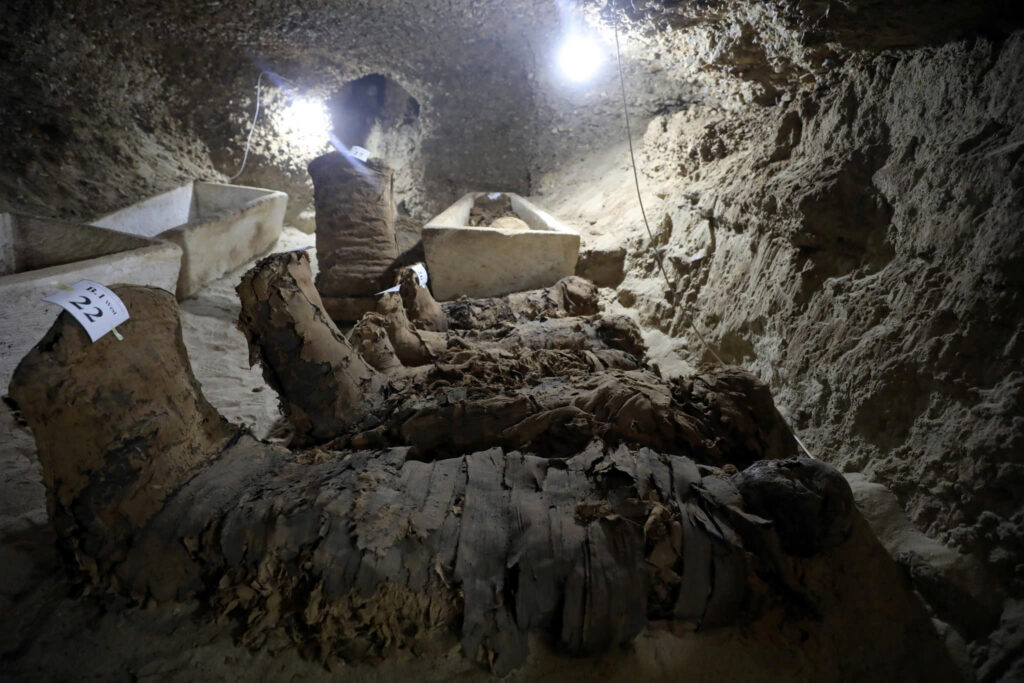

During the Industrial Revolution, the exploitation of mummies reached new heights. Large quantities were ground into powder for use as agricultural fertilizer in Britain and Germany. Even more shocking, some mummies were reportedly burned as fuel for locomotives, reducing sacred remains to mere combustible material.
Paper Production and Pigments

Mummy wrappings found their way into paper production in the United States, while a unique pigment called “mummy brown,” made from ground mummy remains, became popular among artists. This pigment, prized for its transparent qualities and rich earthy tones, was used in paintings until the 20th century.
The Counterfeit Trade
As supplies of genuine ancient mummies dwindled, a disturbing practice emerged. Unscrupulous traders began creating fake mummies using the bodies of the recently deceased. These bodies were crudely preserved using bitumen and sun-drying techniques to mimic the appearance of ancient mummies, further degrading the dignity of both the ancient and recent dead.
Legacy and Modern Perspective
Today, this Victorian-era trade serves as a sobering reminder of how historical artifacts and human remains were once carelessly exploited. The practice ended as supplies diminished and ethical awareness grew. The discontinuation of products like mummy brown pigment marks society’s evolving respect for cultural heritage and human dignity.
The story of Egypt’s mummy trade stands as a cautionary tale about the importance of preserving and respecting historical artifacts and human remains. It reminds us how easily cultural treasures can be degraded when viewed solely through the lens of commerce and entertainment.

