A Marvel of Ancient Engineering
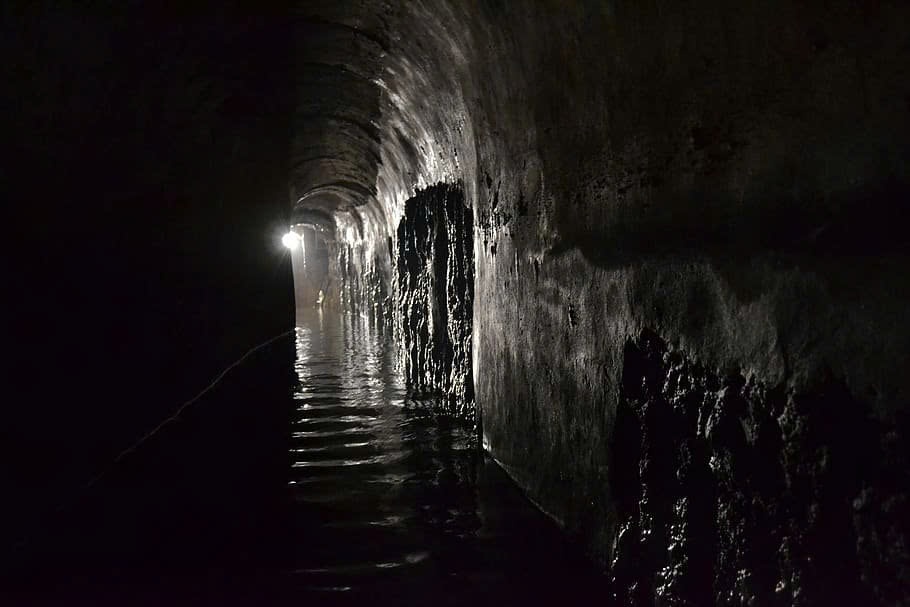

In the annals of human engineering, few achievements rival the ingenuity and scale of the Roman aqueducts. While the Colosseum and grand arches often steal the spotlight, it’s the vast network of underground waterways that truly showcases Roman brilliance. These subterranean marvels, accounting for a staggering 80% of Rome’s total aqueduct length, were the invisible arteries that nourished the empire’s heart and its far-flung provinces.
The Birth of an Underground Revolution
Our story begins in 312 BC with the construction of the Aqua Appia, Rome’s first aqueduct. As the city’s thirst grew with its expanding population, engineers faced a challenge: how to supply clean, abundant water to every corner of the burgeoning metropolis? The answer lay beneath their feet.
Engineering Feats in the Shadows
Picture this: a team of Roman engineers, armed with nothing but rudimentary tools and an unparalleled understanding of gravity, carving channels through earth and rock. These underground passages were not mere tunnels; they were precision-engineered conduits, maintaining a gentle slope to ensure water flowed consistently from source to city.

To protect their liquid treasure, the Romans lined these channels with a special water-resistant mortar called “opus signinum.” This foresight ensured that the water remained pure and the structures endured, outlasting many of their above-ground counterparts.
A Strategic Masterpiece
But why hide such an impressive feat underground? The reasons were as practical as they were strategic. Buried deep, these aqueducts were shielded from enemy attacks and natural disasters. Moreover, the cool earth prevented water loss through evaporation, a crucial advantage during Rome’s sweltering summers.
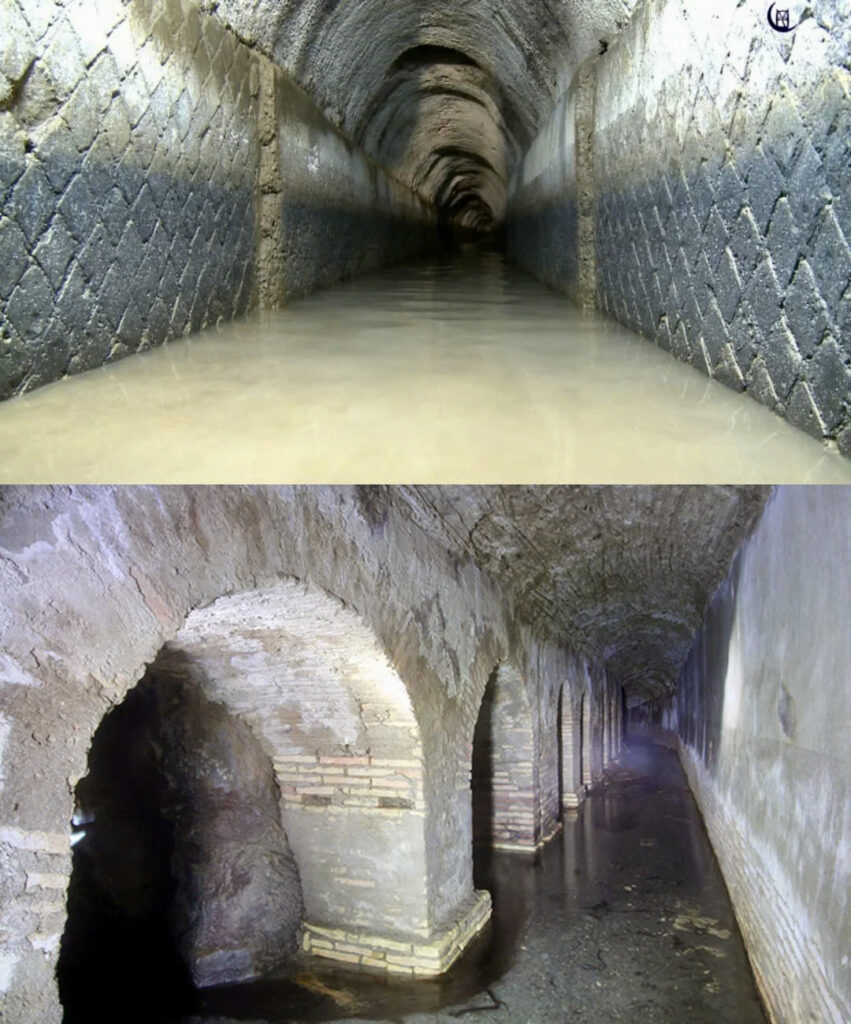

From Capital to Empire
While Rome itself boasted impressive aqueducts like the Aqua Claudia and Aqua Marcia, this engineering marvel wasn’t confined to the capital. From Segovia in Spain to Ephesus in modern-day Turkey, major cities across the empire benefited from this Roman ingenuity. These aqueducts became symbols of Roman might and the tangible benefits of its governance.
More Than Just Water
The impact of these hidden highways of water extended far beyond mere hydration. They fed the public baths, the beating heart of Roman social life. They supplied the fountains where citizens gathered to gossip and trade. In essence, they democratized access to one of life’s most vital resources, reinforcing the Roman state’s commitment to its citizens’ welfare.
A Legacy Unearthed
As the empire declined, much of this intricate system fell into disrepair. Yet, some sections, like the Aqua Virgo in Rome, continue to function to this day, feeding iconic landmarks like the Trevi Fountain. Recent urban projects and archaeological digs have brought more of this hidden network to light, reminding us of the enduring legacy of Roman engineering.
Conclusion
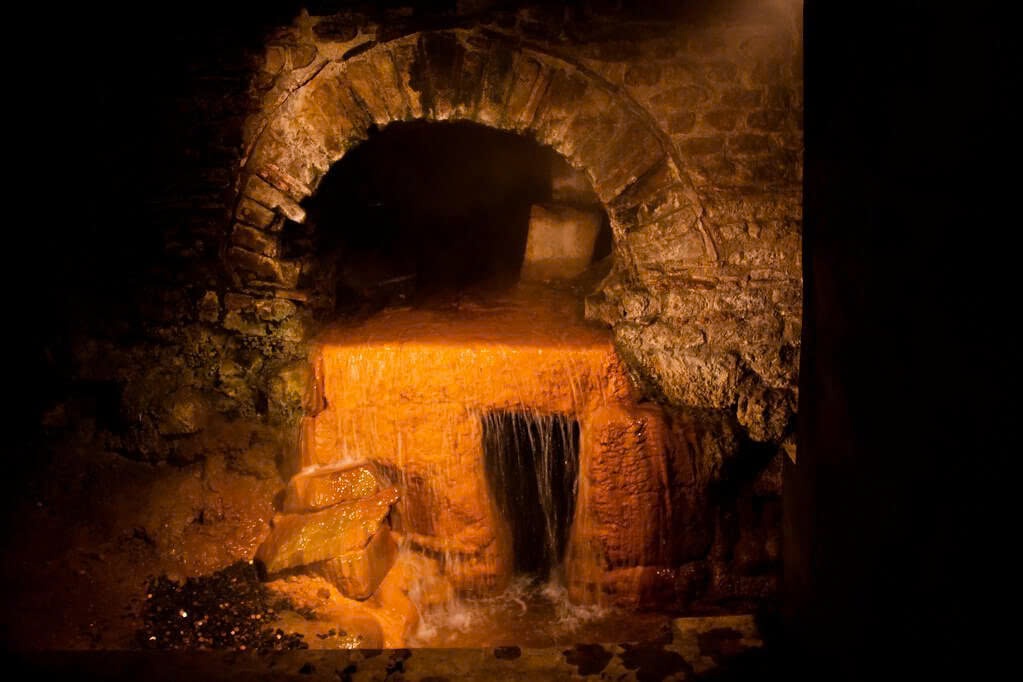

The story of Rome’s underground aqueducts is one of vision, skill, and lasting impact. These hidden veins of the empire stand as a testament to a civilization that, at its peak, seamlessly blended form and function. They remind us that true greatness often lies not in what’s visible, but in the unseen foundations that support grand achievements. As we walk beneath the shadows of aqueduct arches or marvel at the fountains they feed, we’re witnessing the enduring legacy of Roman ingenuity – a legacy that continues to flow through the veins of modern civilization.

