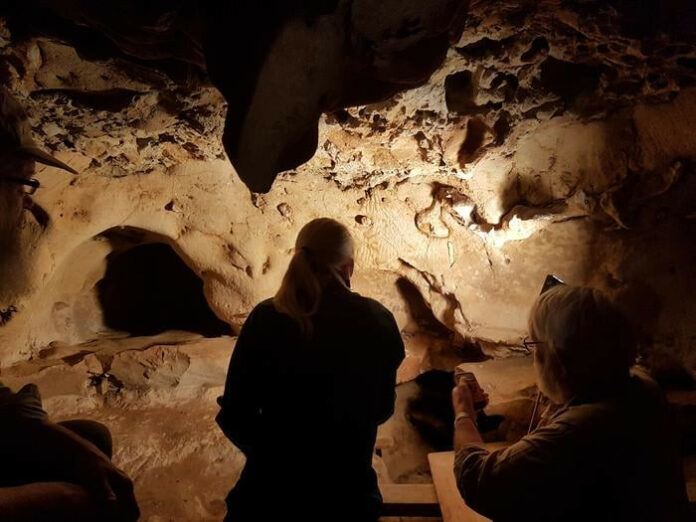
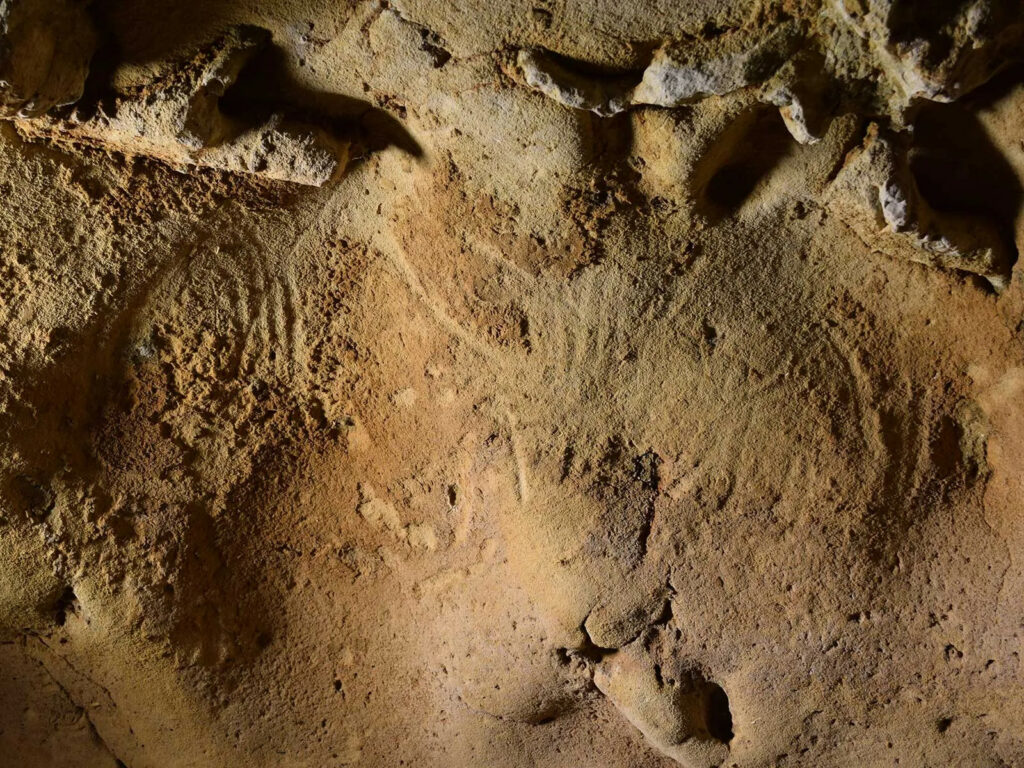
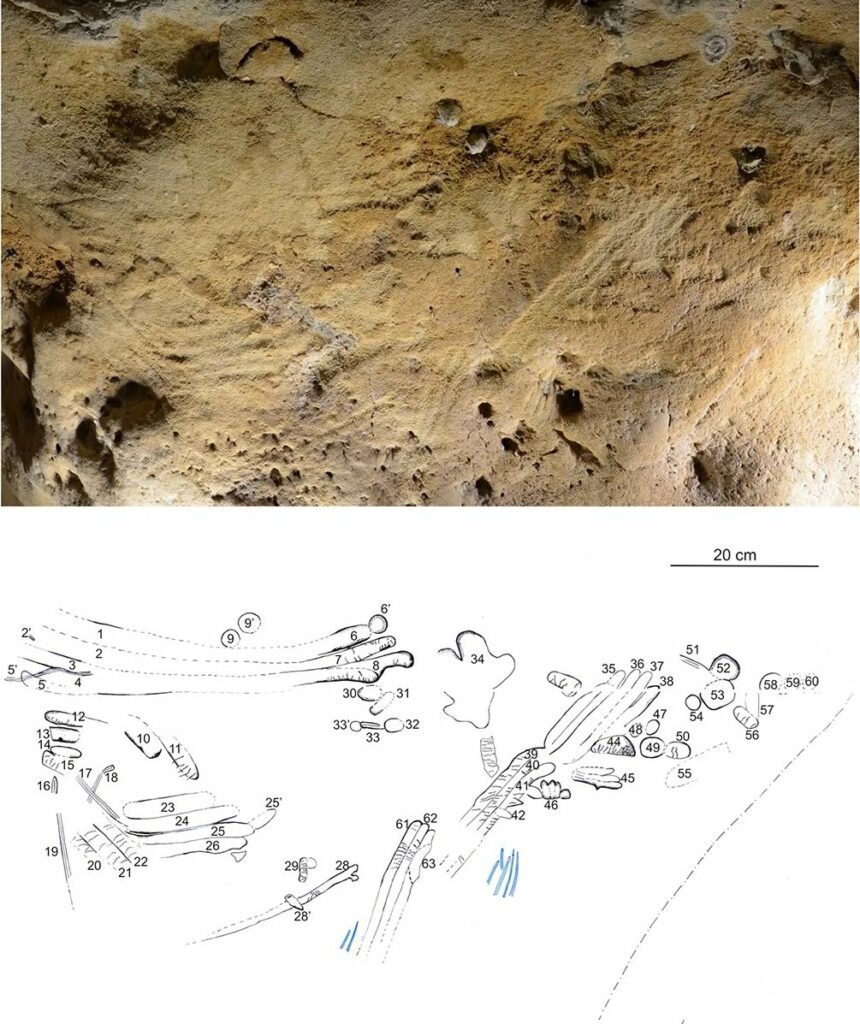
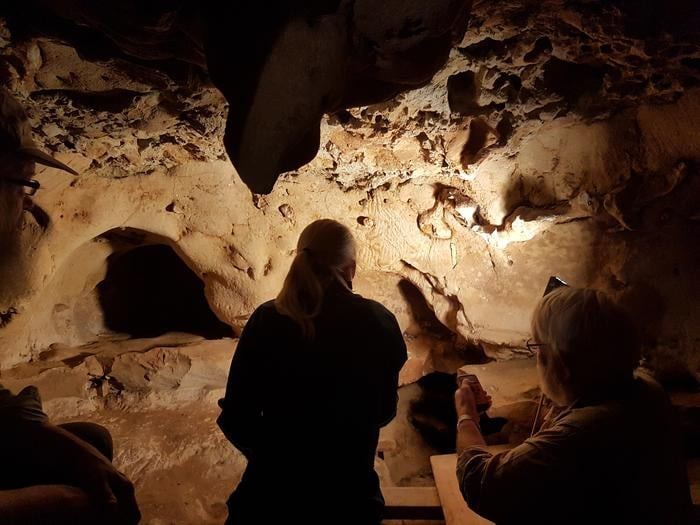
In a cave nestled in the hillsides above France’s Loire Valley, Paleolithic humans once stood before a soft, chalky wall over 57,000 years ago. Using their fingers, they deliberately carved enduring lines and dots into the rock face. These creative markings would remain sealed within the cave for tens of thousands of years – until now.
Oldest Known Neanderthal Engravings
Scientists have determined that these patterned engravings are the oldest known example of Neanderthal cave art. By analyzing the markings, comparing them to other prehistoric art, and dating the sediment layers that had buried the cave entrance, researchers concluded the engravings were made between 57,000-75,000 years ago – long before modern Homo sapiens inhabited this region.

New Insights into Neanderthal Capabilities
The discovery adds to growing evidence that Neanderthals, our closest ancestors, were more cognitively advanced than the simplistic caveman stereotypes suggest. The structured, intentional nature of the engravings indicate they were carefully planned and executed, not hastily made. While the meaning behind the abstract shapes remains unknowable, their existence alone provides a fascinating glimpse into the inner lives of these vanished peoples.
Converging Evidence Points to Neanderthal Artists
Multiple lines of evidence allowed archaeologists to attribute the cave art to Neanderthals:
- The cave contained a trove of distinctly Neanderthal stone tools
- Sediment layers showed the cave had been sealed off at least 57,000 years ago, before Homo sapiens arrived
- Analysis confirmed the markings were deliberately engraved by human fingers
While comparisons to later Homo sapiens cave paintings may be tempting, scholars believe the impetus for creating such art depended more on the social needs of the time rather than inherent differences in ability between the two human species. This incredible find provides just one more tantalizing clue to help us understand the rich inner worlds of our long-lost relatives.


